UVM介绍 UVM即Universal Verification Methodology,他是在VMM(Verification Methodology Manual)、OVM(OpenVerification Methodology)后于2011年2月发布的。
UVM目的在于提供一些可重用的类用来减轻项目之间的水平复用和垂直复用的工作量。
UVM涵盖了从模块级到芯片级,ASIC到FPGA,以及控制逻辑、数据通路到处理器验证对象的全部场景。
UVM的整体结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 task run_test(string test_name="" );.get_root ();.run_test (test_name);endtask
上述代码是uvm的顶层,它构造了uvm_root并且运行测试test_name,即运行uvm_test的实例
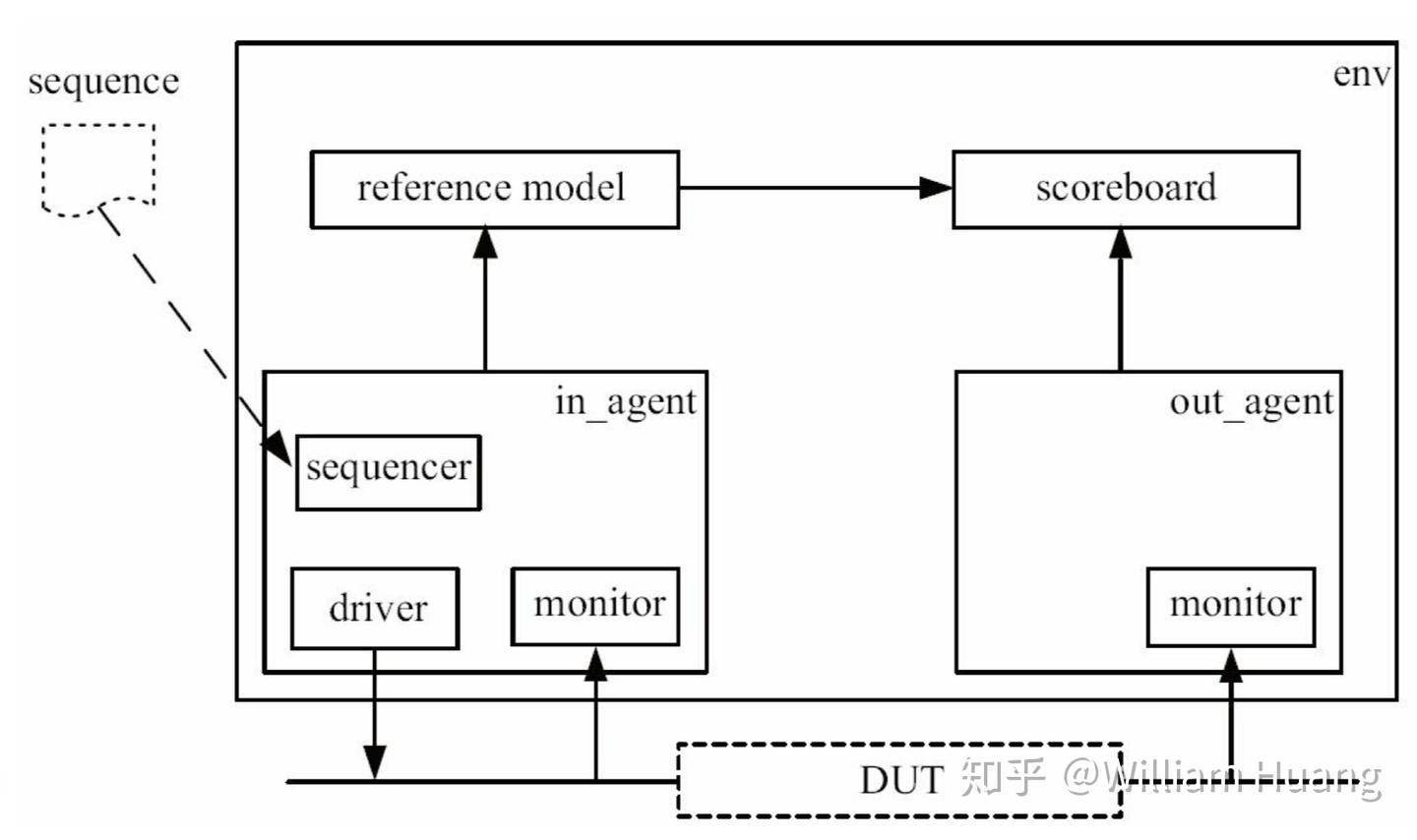
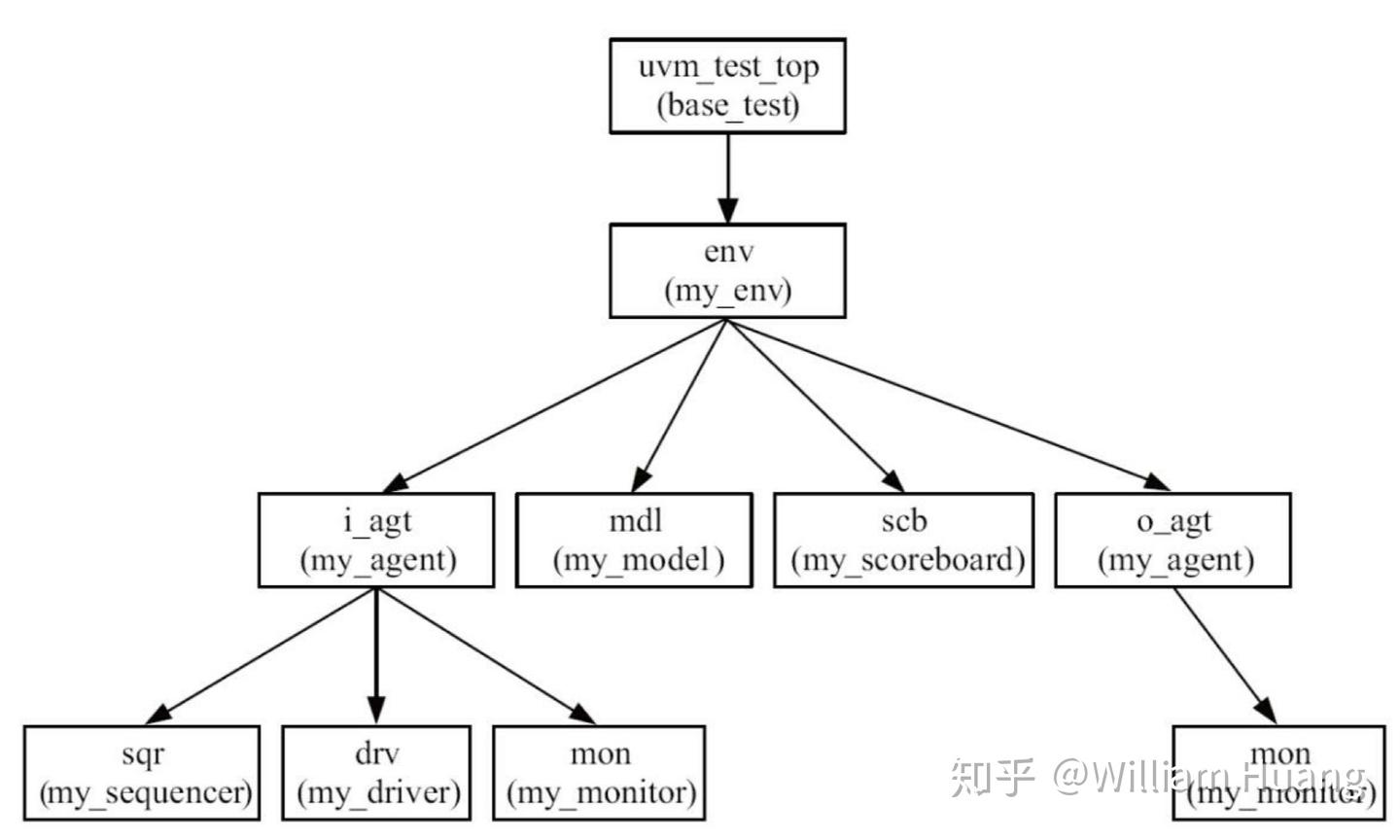
如上图所示uvm_test中包含uvm_env,而uvm_env中包含一些测试工具,用于产生测试用例并与DUT进行对照
UVM组件 uvm_sequence uvm_sequence_item为测试数据包,可以提供一些打印克隆等函数。而uvm_sequence将生成一系列item并发送给测试系统。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class gen_item_seq extends uvm_sequence;function new (string name="gen_item_seq" );super .new (name);endfunction rand int num; constraint c1 { soft num inside {[2 :5 ]}; }virtual task body();for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i ++) begin "m_item" );.randomize ();"SEQ" , $sformatf ("Generate new item: " ), UVM_LOW).print ();end "SEQ" , $sformatf ("Done generation of %0d items" , num), UVM_LOW)endtask endclass class reg_item extends uvm_sequence_item;rand bit [`ADDR_WIDTH-1 :0 ] addr;rand bit [`DATA_WIDTH-1 :0 ] wdata;rand bit wr;bit [`DATA_WIDTH-1 :0 ] rdata;virtual function string convert2str();return $sformatf ("addr=0x%0h wr=0x%0h wdata=0x%0h rdata=0x%0h" , addr, wr, wdata, rdata);endfunction function new (string name = "reg_item" );super .new (name);endfunction endclass
uvm_sequencer 用于接收发送过来的sequence_item
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class my_sequencer extends uvm_sequencer#(basic_transaction) ;function new (string name,uvm_component parent) ;super .new (name,parent) ;endfunction :new endclass :my_sequencer
uvm_driver 将数据包发送给DUT(虚接口),通过get_next_item可以获得下一个数据包,seq_item_port就是sequencer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class driver extends uvm_driver #(reg_item) ;function new (string name = "driver" , uvm_component parent=null );super .new (name, parent);endfunction virtual reg_if vif; virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .build_phase (phase);if (!uvm_config_db#(virtual reg_if)::get(this, "", "reg_vif", vif)) "DRV" , "Could not get vif" )endfunction virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .run_phase (phase);forever begin "DRV" , $sformatf ("Wait for item from sequencer" ), UVM_LOW).get_next_item (m_item); .item_done ();end endtask virtual task drive_item(reg_item m_item);.sel <= 1 ;.addr <= m_item.addr ;.wr <= m_item.wr ;.wdata <= m_item.wdata ;posedge vif.clk );while (!vif.ready ) begin "DRV" , "Wait until ready is high" , UVM_LOW)posedge vif.clk );end .sel <= 0 ;endtask endclass
uvm_monitor 用于监听DUT的信号并将其发送给scoreboard
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class monitor extends uvm_monitor;function new (string name="monitor" , uvm_component parent=null );super .new (name, parent);endfunction #(reg_item) mon_analysis_port;virtual reg_if vif;virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .build_phase (phase);if (!uvm_config_db#(virtual reg_if)::get(this, "", "reg_vif", vif)) "MON" , "Could not get vif" )new (1 );new ("mon_analysis_port" , this );endfunction virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .run_phase (phase);forever begin posedge vif.clk );if (vif.sel ) begin new ;.addr = vif.addr ;.wr = vif.wr ;.wdata = vif.wdata ;if (!vif.wr ) begin posedge vif.clk );.rdata = vif.rdata ;end $sformatf ("Monitor found packet %s" , item.convert2str ()), UVM_LOW).write (item); end end endtask endclass
uvm_agent 用于连接monitor、driver、sequencer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class agent extends uvm_agent;function new (string name="agent" , uvm_component parent=null );super .new (name, parent);endfunction #(reg_item) s0; virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .build_phase (phase);#(reg_item)::type_id::create("s0", this) ;"d0" , this );"m0" , this );endfunction virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .connect_phase (phase);.seq_item_port .connect (s0.seq_item_export ); endfunction endclass
uvm_scoreboard 当从monitor接收到信息之后会调用函数write来进行处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class scoreboard extends uvm_scoreboard;function new (string name="scoreboard" , uvm_component parent=null );super .new (name, parent);endfunction #(reg_item, scoreboard) m_analysis_imp;virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .build_phase (phase);new ("m_analysis_imp" , this );endfunction virtual function write(reg_item item);if (item.wr ) begin if (refq[item.addr ] == null ).addr ] = new ;.addr ] = item;$sformatf ("Store addr=0x%0h wr=0x%0h data=0x%0h" , item.addr , item.wr , item.wdata ), UVM_LOW)end if (!item.wr ) begin if (refq[item.addr ] == null )if (item.rdata != 'h1234 )$sformatf ("First time read, addr=0x%0h exp=1234 act=0x%0h" ,.addr , item.rdata ))else $sformatf ("PASS! First time read, addr=0x%0h exp=1234 act=0x%0h" ,.addr , item.rdata ), UVM_LOW)else if (item.rdata != refq[item.addr ].wdata )$sformatf ("addr=0x%0h exp=0x%0h act=0x%0h" ,.addr , refq[item.addr ].wdata , item.rdata ))else $sformatf ("PASS! addr=0x%0h exp=0x%0h act=0x%0h" ,.addr , refq[item.addr ].wdata , item.rdata ), UVM_LOW)end endfunction endclass
uvm_env 连接agent和scoreboard
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class env extends uvm_env;function new (string name="env" , uvm_component parent=null );super .new (name, parent);endfunction virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .build_phase (phase);"a0" , this );"sb0" , this );endfunction virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .connect_phase (phase);.m0 .mon_analysis_port .connect (sb0.m_analysis_imp );endfunction endclass
uvm_test 负责初始化及运行测试环境
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class test extends uvm_test;function new (string name = "test" , uvm_component parent=null );super .new (name, parent);endfunction virtual reg_if vif;virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);super .build_phase (phase);"e0" , this );if (!uvm_config_db#(virtual reg_if)::get(this, "", "reg_vif", vif)) "TEST" , "Did not get vif" )#(virtual reg_if)::set(this, "e0.a0.*", "reg_vif", vif) ;endfunction virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);"seq" );.raise_objection (this ); .randomize () with {num inside {[20 :30 ]}; };.start (e0.a0 .s0 );200 ;.drop_objection (this );endtask virtual task apply_reset();.rstn <= 0 ;repeat (5 ) @ (posedge vif.clk );.rstn <= 1 ;repeat (10 ) @ (posedge vif.clk );endtask endclass
工厂与初始化
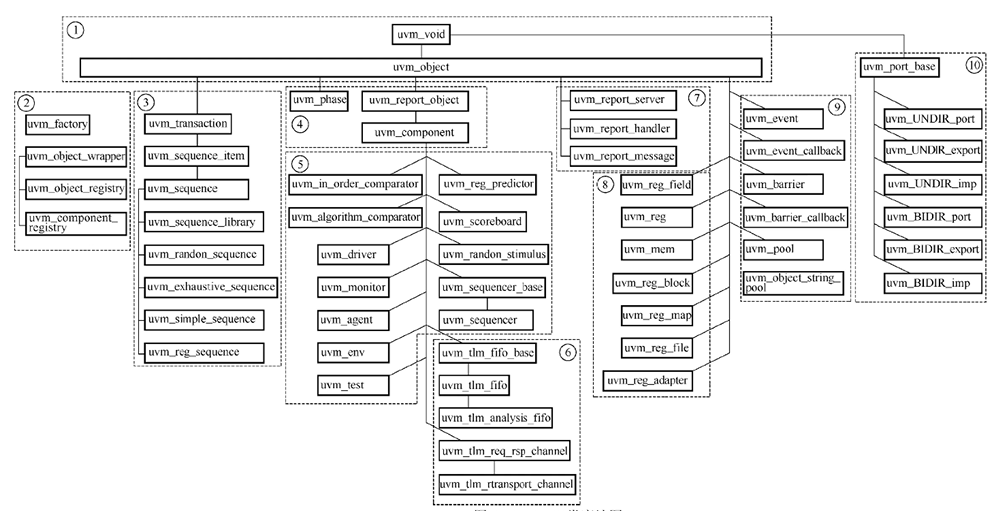
uvm_component派生于uvm_object,用于构建uvm环境(uvm_tree)。它包括hierarchy系列函数(查找组件成员)、phase系列(进行仿真)、repost系列(输出打印)、factory系列(创建实例)。
uvm_object和uvm_component区别 :
uvm_component必须通过create创建,uvm_object可以通过new/create创建
uvm_component存在于验证的整个过程中,始终不会析构。而uvm_object可以被动态的创建和析构
uvm_component构造时需要指定parent,而uvm_object不需要
1 2 3 4 string name, uvm_component parent);string name);
在上文中构造uvm_item_seq时调用了uvm_object_utils(gen_item_seq),在此之中便将类注册到工厂中。工厂类位于uvm_coreservice_t类中,在最开始的例子中通过uvm_coreservice_t::get()获得这个类的instance。
uvm_coreservice_t中主要包括:
唯一的uvm_factory
全局的report_server,负责消息统筹与报告
全局的tr_database,负责记录transaction
get_root()获得当前uvm环境的根节点
uvm提供了一个重要特性覆盖 ,他可以使得子类替换父类,当实例化父类时实际上实例化子类。
覆盖发生时,可以使用类型覆盖或实例覆盖。
类型覆盖: UVM层次结构下所有原有类型会被覆盖类型替换
实例覆盖: 某些位置原有类型会被覆盖类型替换
相关函数:
set_type_override(uvm_object_wrapper override_type, bit replace=1): replace表示如果有覆盖存在,当前设置是否替换原有覆盖,类型可以使用new_type::get_type()获得
set_inst_override(uvm_object_wrapper override_type, string inst_path, uvm_component=null):
例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 module factory_override;import uvm_pkg::*;`include "uvm_macros.svh" class comp1 extends uvm_component;function new (string name="comp1" , uvm_component parent=null );super .new (name, parent);$display ($sformatf ("comp1:: %s is created" , name));endfunction :new virtual function void hello(string name);$display ($sformatf ("comp1:: %s said hello!" , name)) ;endfunction endclass class comp2 extends comp1; function new (string name="comp2" , uvm_component parent=null );super .new (name, parent);$display ($sformatf ("comp2:: %s is created" , name) );endfunction :new function void hello(string name);$display ($sformatf ("comp2:: %s said hello!" , name));endfunction endclass initial begin new ("c1" );"c2" , null );.hello ("c1" );.hello ("c2" );end endmodule
phase phase定义的是uvm代码的执行顺序。由于包含层次化结构,不仅需要判断各个phase的执行顺序,还需要决定同一phase之内各个组件之间的执行顺序。
phase
函数/任务
执行顺序
功能
应用
build
函数
自顶向下
创建和配置测试平台的结构
创建组件和寄存器模型,设置或者获取设置
connect
函数
自底向上
建立组件之间的连接
连接TLM的接口,连接寄存器模型和adapter
end_of_elaboration
函数
自底向上
测试环境微调
显示环境结构、打开文件,为组件添加额外配置
start_of_simulation
函数
自底向上
准备测试环境的仿真
显示环境结构、设置断点,设置初始运行时的配置值
run
任务
自底向上
激励设计
提供激励、采集数据、数据比较
extract
函数
自底向上
从测试环境中收集数据
从测试平台提取剩余数据,从设计观察最终状态
check
函数
自底向上
检查任何不期望的行为
检查不期望的数据
report
函数
自底向上
报告测试数据
报告测试结果并写入文件
final
函数
自顶向下
完成测试活动、结束仿真
关闭文件,结束联合仿真引擎
在run中还可以划分为下面12个phase
pre_reset_phase
reset_phase
post_reset_phase
pre_configure_phase
configure_phase
post_configure_phase
pre_main_phase
main_phase
post_main_phase
pre_shutdown_phase
shutdown_phase
post_shutdown_phase
根据是否消耗仿真时间,可以将phase分为两大类: function phase和task phase。其中function phase不需要消耗仿真时间,如build_phase、connect_phase等。task phase包括run_phase.
config机制 uvm使用uvm_config_db配置类以及几种变量设置方法来实现仿真时环境控制,常见用途包括
传递virtual interface到环境中
设置变量值
传递配置对象(config object)到环境中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 uvm_config_db#(T)::set(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, T value) ;virtual interface ,int ,string ,enum ,config object等#(T)::get(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, inout T value) ;
例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 interface intf1;logic enable = 0 ;endinterface class comp1 extends uvm_component;virtual intf1 vif;function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase) ;if (!uvm_config_db#(virtual intf1)::get(this, "", "vif", vif) ) begin "GETVIF" , "no virtual interface is assigned" )end "SETVAL" , $sformatf ("vif.enable is %b before set" , vif.enable ), UVM_LOW).enable = 1 ;"SETVAL" , $sformatf ("vif.enable is tb after set" , vif.enable ), UVM_LOW)endfunction endclass class test1 extends uvm_test;endclass initial begin #(virtual intf1)::set(uvm_root::get() , "uvm_test_top.c1", "vif", intf) ;"test1" );end
object传递:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class config1 extends uvm_object;int val1 = 1 ;int str1 = "null" ;endclass class comp1 extends uvm_component;function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase) ;#(uvm_object)::get(this, "", "cfg", tmp) ;void '($cast (cfg, tmp));"SETVAL" , $sformatf ("cfg.val1 is %d after get" , cfg.val1 ), UVM_LOW)"SETVAL" , $sformatf ("cfg.str1 is %s after get" , cfg.str1 ) , UVM_LOW)endfunction endclass class test1 extends uvm_test;function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);"cfg1" );"cfg2" );.val1 = 30 ;.strl = "c1" ;.val1 = 50 ;.str1 = "c2" ;#(uvm_object)::set(this, "c1", "cfg", cfg1) ;#(uvm_object)::set(this, "c2", ”cfg”, cfg2) ;"c1" , this );"c2" , this );endfunction endclass
参考