本文最后更新于 2020年4月7日 下午
基本原理
归并排序运用了分治的思想,先将数组二分成一个元素(一个元素时看为有序),然后将这些元素不断合并,每合并一次排一次序,最后就可以得到有序的数组。
比如说一个序列:12 ,23,1,44,233,10,9,8。我们先分成两段:12 ,23,1,44 和 233,10,9,8,
发现还能再分成4段:12 ,23 和 1,44———233,10 和 9,8。
再分成8段:12—23—1—44 和233—10—9—8。
这时候开始把子序列进行排序合并,一个元素就是有序的。所以不用排序。
合并成2个一组排序得到:12,23——1,44—-10,233—-8,9。
再合并成4个一组排序得到:1,12,23,44—-8,9,10,233。
最后合并得到最终结果:1,8,9,10,12,23,44,233。
合并过程看代码
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/b50a6034eb90
图解
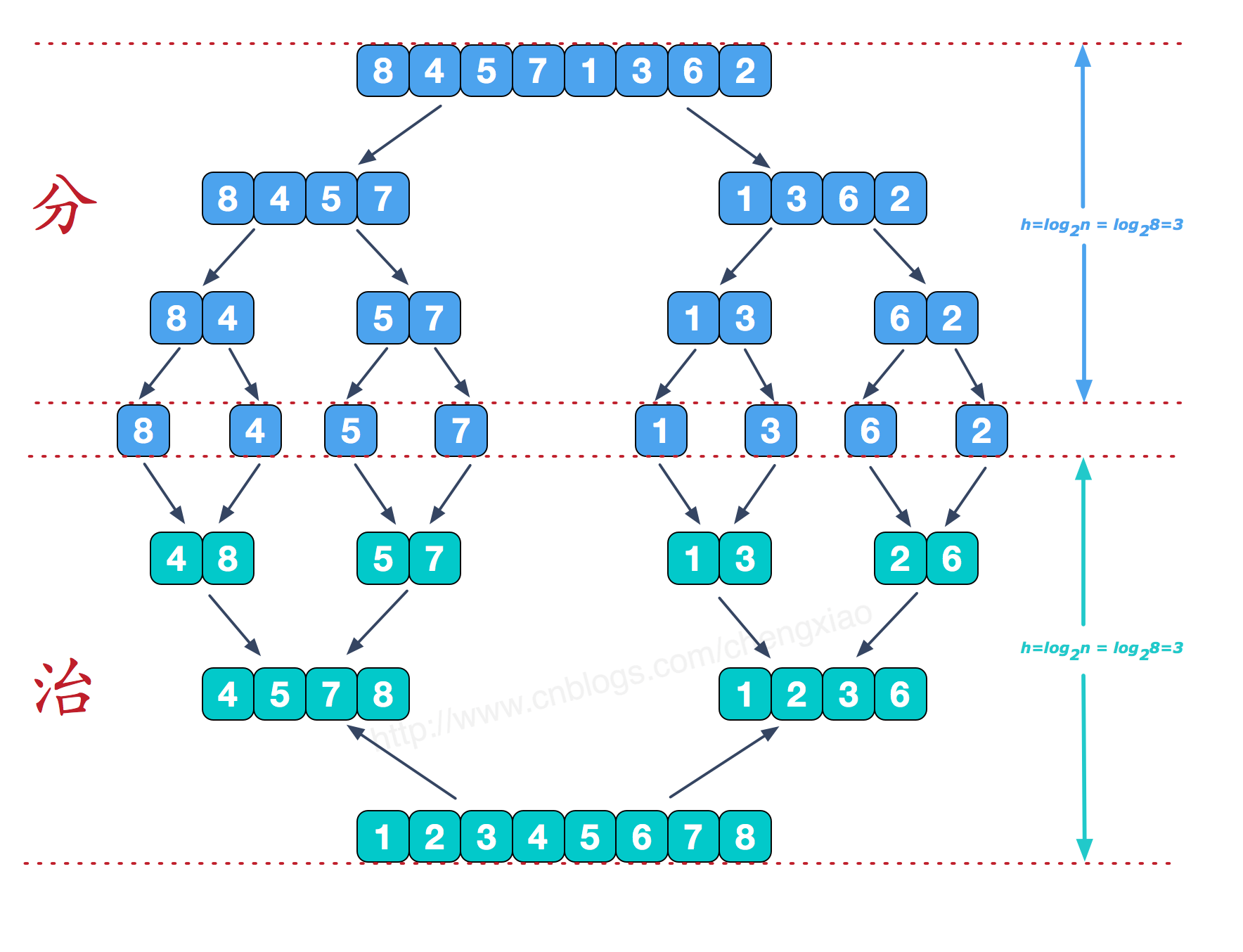
这个图片蓝色部分就是拆的过程,而绿的部分为并的过程
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| void paixu(int first,int mid,int last,int a[],int temp[])//这是合并过程
{
int l1=first,l2=mid+1,r1=mid,r2=last;
int k=0;
while(l1<=r1&&l2<=r2)//两部分都存在时看哪个小就加上哪个
{
if(a[l1]<=a[l2])
{
temp[k++]=a[l1++];
}
else
{
temp[k++]=a[l2++];
}
}
while(l1<=r1)//第一部分有剩余就把第一部分剩下的全加上
{
temp[k++]=a[l1++];
}
while(l2<=r2)
{
temp[k++]=a[l2++];
}
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
{
a[i+first]=temp[i];
}
}
void xunhuan(int first,int last,int a[],int temp[])
{
if(first<last)
{
int mid=(first+last)/2;
xunhuan(first,mid,a,temp);//拆左边
xunhuan(mid+1,last,a,temp);//拆右边
paixu(first,mid,last,a,temp);//合并
}
}
bool mergesort(int a[],int first,int last)
{
int* p=new int[last-first];//建一个临时数组,合并时用
if(p==NULL)//判断是否传入空数组
{
return false;
}
xunhuan(first,last,a,p);
delete [] p;
return true;
}
|
